Restricted, Repetitive, and Reciprocal Social Behavior in Toddlers Born Small for Gestation Duration.
Abstract
Objective To characterize restricted and repetitive behaviors (RRBs) and reciprocal social behaviors (RSBs) in a large sample of toddlers who represent a range of birth weights and gestation durations.
Study design A battery of questionnaires characterizing demographic information and measuring RRBs and RSBs were completed by parents of toddlers between the ages of 17-26 months (n = 1589 total; n = 98 preterm). The association between birth weight and/or gestation duration and the primary outcome measures (RRBs and RSBs as ascertained through the Repetitive Behavior Scale for Early Childhood and the Video-Referenced Rating of Reciprocal Social Behavior) were tested by using hierarchical multivariate multiple regression.
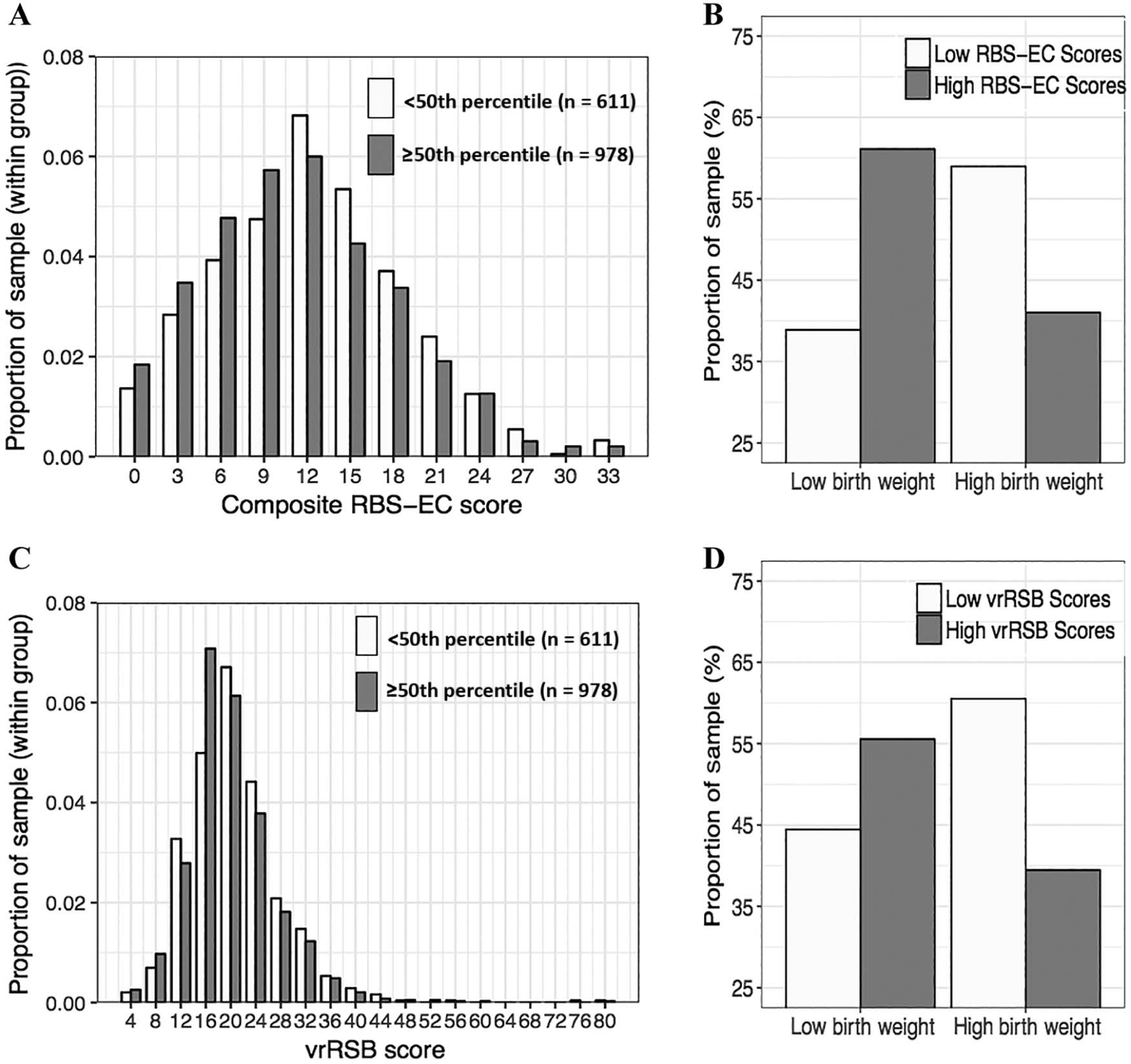
Results Toddlers born preterm and full term did not differ on RRBs or RSBs. However, there were significant associations between birth weight percentile for gestation duration (BPGD) and RRBs (b = −2.1, P = .03), above and beyond the effects of age, sex, and vocabulary production. Similarly, there was a significant association between BPGD and RSBs. (b= −1.8, P = .02), above and beyond the effects of age, sex, and vocabulary production.
Conclusions These findings demonstrate that BPGD better predicted putative antecedents of adverse psychological outcomes—specifically, RRBs and RSBs—than gestation duration alone. These findings provide insight to the link between preterm birth and suboptimal behavioral/psychological outcomes and suggest that high birth weight, which may reflect a more optimal intrauterine environment, may serve as a protective factor irrespective of gestation duration.
 |