A Longitudinal Investigation of Preferential Attention to Biological Motion in 2- to 24-Month-Old Infants
Abstract
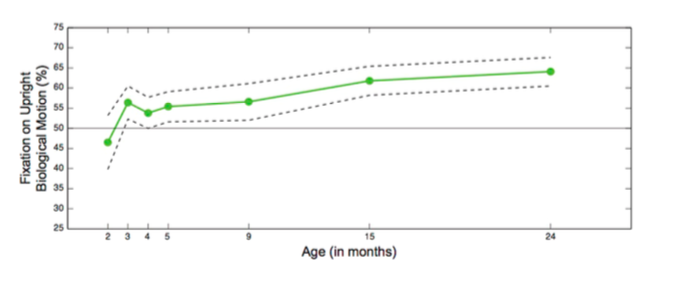
Preferential attention to biological motion is an early-emerging mechanism of adaptive action that plays a critical role in social development. The present study provides a comprehensive longitudinal mapping of developmental change in preferential attention to biological motion in 116 infants at 7 longitudinal time points. Tested repeatedly from 2 until 24 months of age, results reveal that preferential attention to biological motion changes considerably during the first months of life. Previously reported preferences in both neonates and older infants are absent in the second month but do reemerge by month 3 and become increasingly pronounced during the subsequent two years. These results highlight the second month of life as a potentially critical transition period in social visual engagement..
 |